Quick Reads
Quick Reads are short guides that introduce key ideas in computing education and highlight practical, research-backed insights. Each one gives you a simple visual overview, clear takeaways, and links to explore further, so you can add new ideas to your teaching practice with ease.
For deeper analysis, you could also read our long-form reports.

ABC learning design
Blended learning offers flexibility, but can be difficult to map out effectively for a diverse cohort. This Quick Read explores how to use a rapid, hands-on storyboarding approach to structure varied learning activities into a cohesive experience for learners, ensuring all six learning types are represented.
Download PDF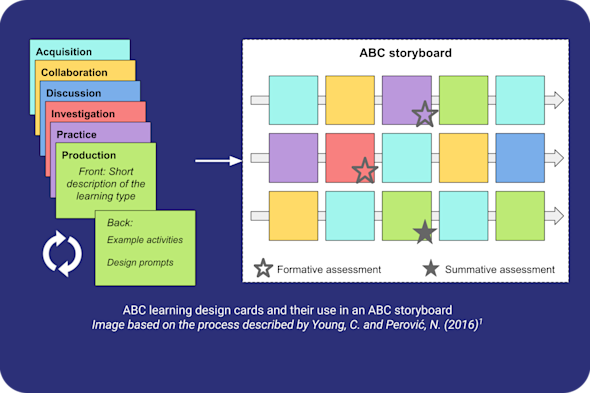
Alternative conceptions
Misconceptions in computing are often 'invisible' and can undermine a learner's progress if they go unaddressed. This Quick Read explores how to identify these simplified or inaccurate beliefs early on, providing you with strategies to build more robust and accurate mental models for your learners.
Download PDF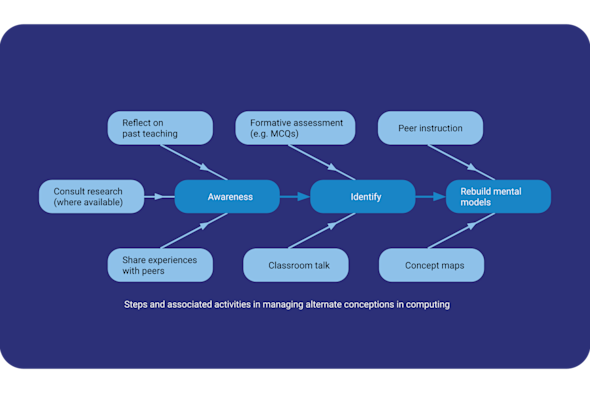
Anthropomorphisation
Learners often mistake AI for having human-like thoughts or intentions, which leads to a lack of critical technical understanding and a potential loss of user agency. This Quick Read explores how to avoid anthropomorphising AI systems, ensuring learners understand their true capabilities and maintain a critical perspective on how they function.
Download PDF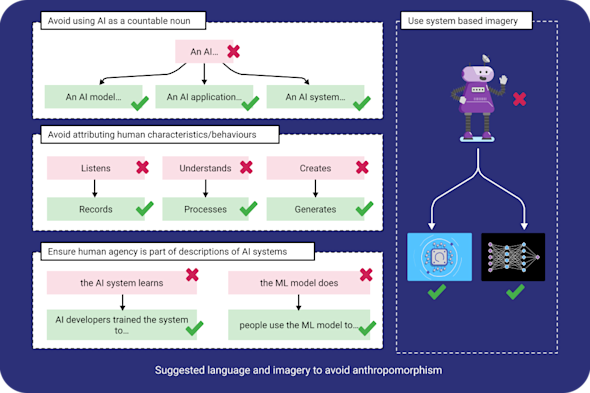
The block model
Reading and understanding code is a key step before you can write high-quality code on your own. However, it can be tempting to skip this step and dive straight into creating code with your learners. This Quick Read explores how to use the block model to prioritise program comprehension, ensuring that your learners can read code prior to writing it.
Download PDF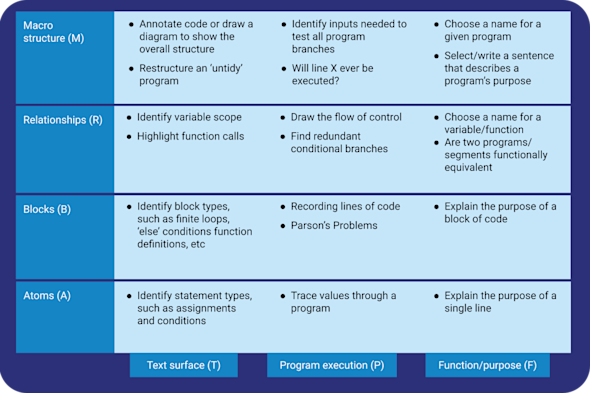
Code tracing
Learners often run code immediately without actually understanding the underlying logic or the step-by-step flow of the program. This Quick Read explores how to use code tracing techniques to help learners predict outcomes and develop a much deeper, structural understanding of how their code actually operates.
Download PDF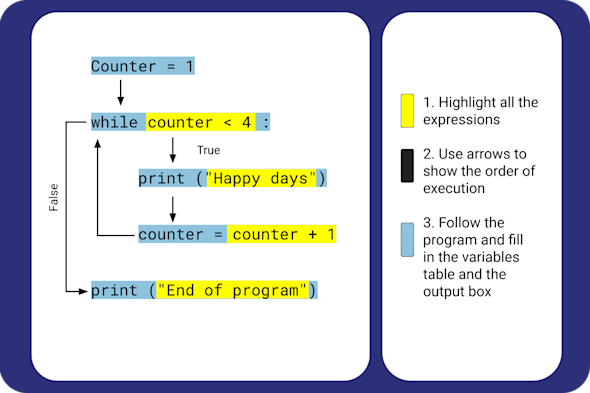
Cognitive load theory
Avoid overwhelming your learners’ working memory. This Quick Read explores how to design teaching materials that carefully manage cognitive load, allowing you to structure information and tasks in a way that maximises learners retention.
Download PDF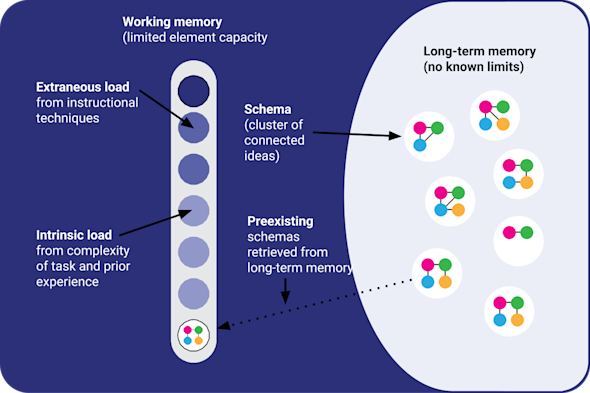
Computational thinking 2.0
As AI and machine learning evolve, traditional rule-based logic is no longer enough for learners to navigate and understand modern digital systems. This Quick Read explores how to bridge the gap between traditional rule-based thinking and today's increasingly important data-driven computational paradigms.
Download PDF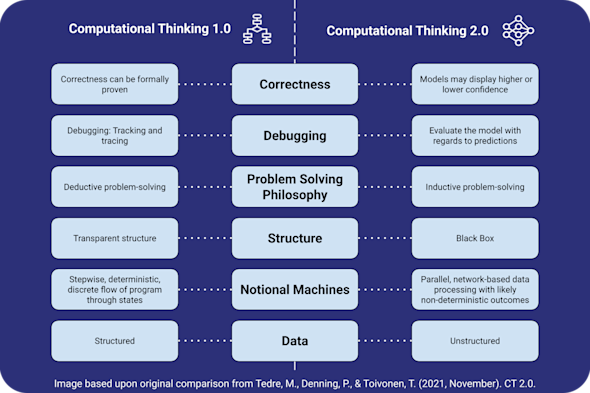
Concept maps
It can be difficult for both educators and learners to visualise and communicate how complex, interconnected computing topics truly relate to one another. This Quick Read explores how to use concept maps to capture, communicate, and assess learners knowledge, providing a clear visual framework for understanding high-level relationships.
Download PDF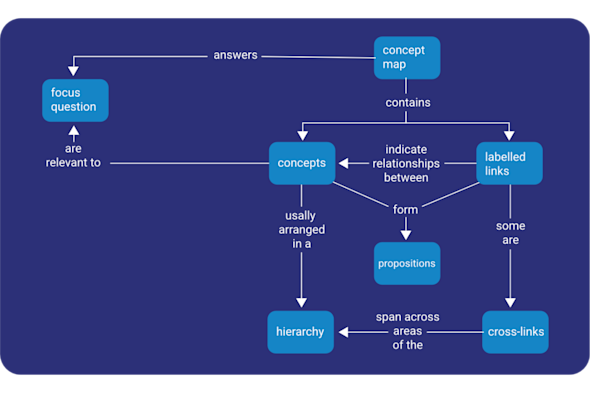
Culturally relevant pedagogy
Computing curricula can sometimes feel disconnected from the diverse lived experiences, backgrounds, and interests of learners. This Quick Read explores how to reflect on your curriculum and materials to make computing more relevant, engaging, and accessible to every learner in your classroom.
Download PDF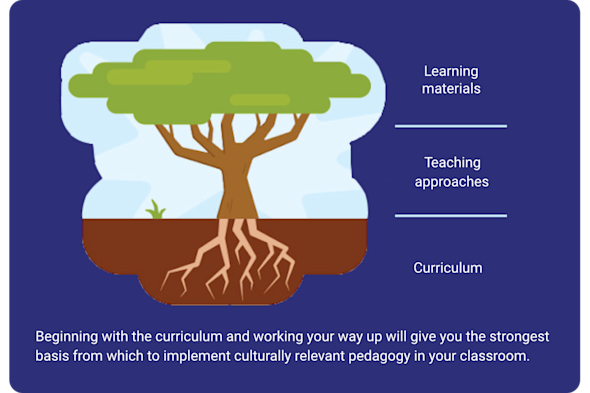
Culturally relevant pedagogy: 10 areas of opportunity
Many educators want to make their computing lessons more inclusive and representative but are often unsure of where to start or what specifically to change. This Quick Read highlights 10 specific 'areas of opportunity' to audit and improve your curriculum, teaching materials, and classroom practices.
Download PDF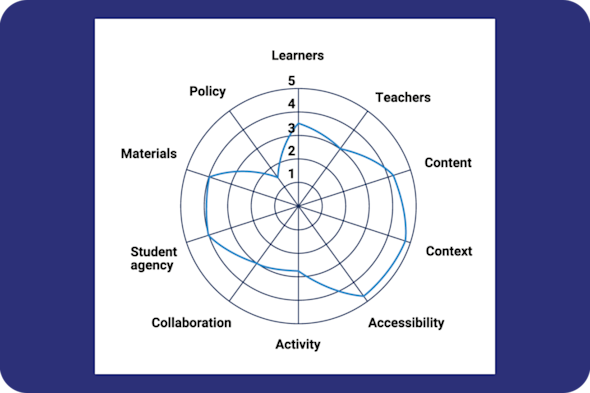
Distance learning
The COVID-19 pandemic forced a shift to 'emergency remote teaching'. As remote and hybrid approaches become commonplace, this Quick Read explores how to plan and reflect on distance learning strategies that maintain instructional quality and keep learners motivated while they are learning from afar.
Download PDF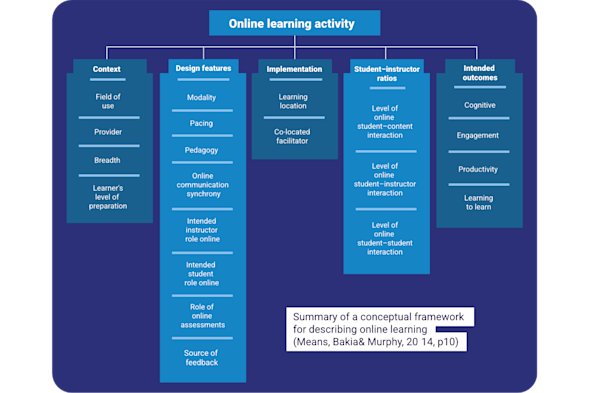
Feedback literacy
Learners increasingly need to know how to critically interact with and evaluate AI-generated feedback or complex outputs. This Quick Read explores how to use a feedback literacy framework to design learning activities where learners engage deeply and critically with the outputs of AI systems.
Download PDF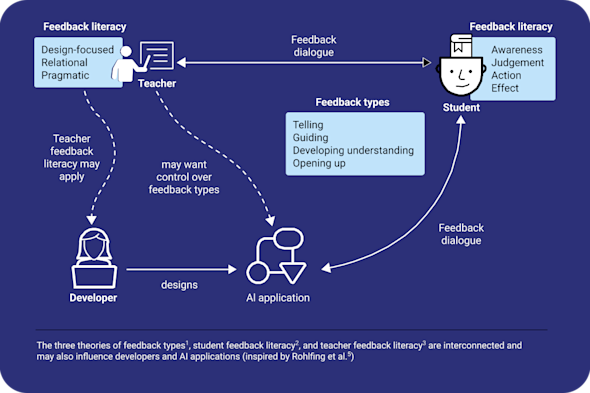
Learning graphs
Linear topic lists often fail to show how specific skills and concepts build, connect, and reinforce each other over a long-term sequence of learning. This Quick Read explores how to use learning graphs to visualise non-linear progression, helping you plan more structured and meaningful lesson sequences.
Download PDF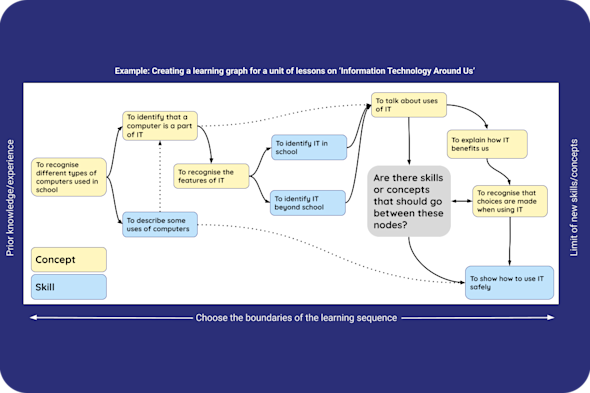
Levels of abstraction in programming
Help your learners see the bigger picture or the abstract problem they are solving, rather than getting 'stuck' in the low-level details of syntax and code. This Quick Read explores how you can encourage your learners to fluidly move between different levels of abstraction, enabling them to become more sophisticated problem solvers.
Download PDF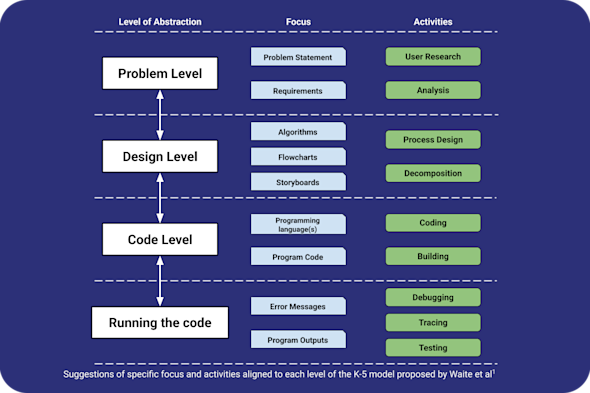
Live coding
Seeing a finished, perfect solution can be intimidating for novices who don't see the 'messy' middle steps or the inevitable errors that occur. This Quick Read explores how to use live coding to model the real-time thought process, debugging steps, and problem-solving journey — mistakes and all! — right in front of your class.
Download PDF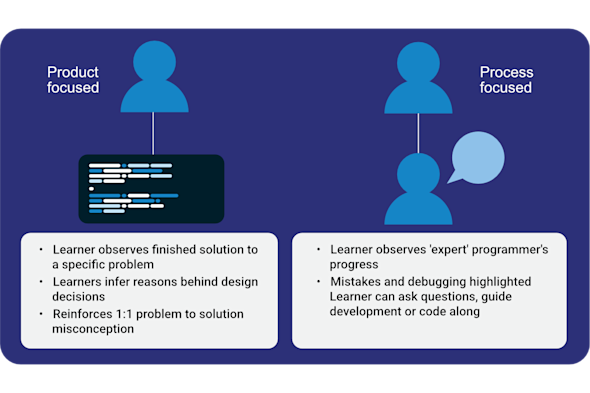
Observations
Educators often struggle to objectively track changes in student behavior during lessons or as a result of new teaching strategies. This Quick Read introduces various observation techniques such as structured live tallies and 'think aloud' verbal protocols to capture clear evidence of learner progress and problem-solving strategies in the computing classroom.
Download PDF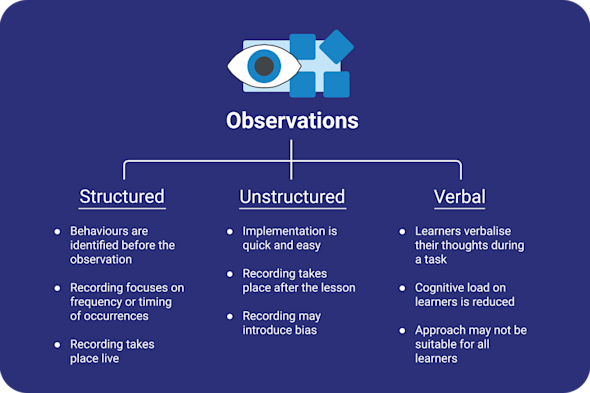
Pair programming
Programming alone as a beginner can lead to a high cognitive load and significant frustration. This Quick Read explores how to overcome this by using pair programming to effectively foster collaboration, reduce the 'fear of failure', and improve the overall quality of your learners’ code.
Download PDF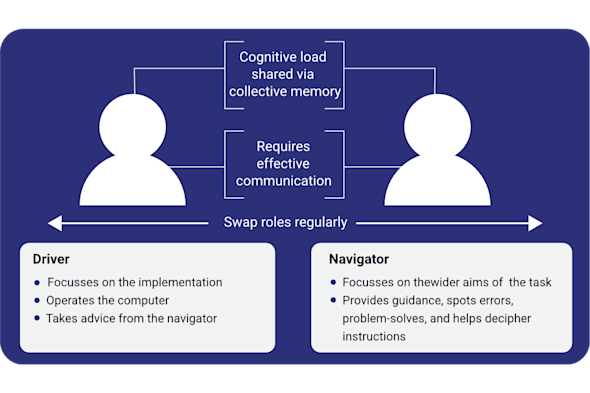
Parson's problems
Writing code from scratch can be a cognitively demanding task that often discourages beginners before they have even started. This Quick Read explores how to use Parson’s Problems to build program comprehension and confidence by having learners 'rebuild' and reorder existing code logic to achieve a goal.
Download PDF
Peer instruction
Meaningful, high-quality classroom dialogue can be an excellent way to reinforce difficult technical concepts, however facilitating such conversations can be tricky. This Quick Read explores how to use structured peer instruction to encourage learners to explain their thinking, debate solutions, and retain complex ideas through peer-to-peer discussion.
Download PDF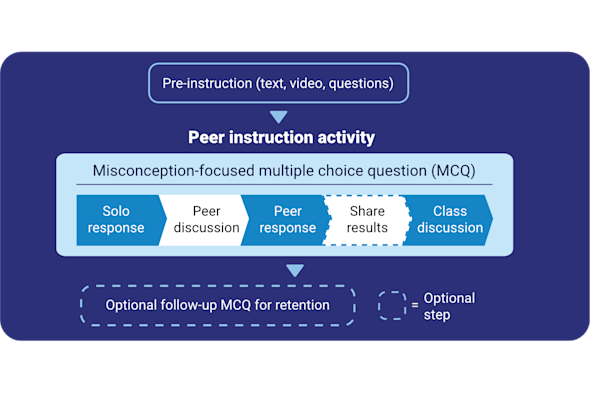
Physical computing
Physical computing can make abstract concepts real for your learners. This Quick Read explores how to embed physical hardware and sensors into your practice to create highly engaging, inclusive, and 'hands-on' learning moments that bring computing concepts to life.
Download PDF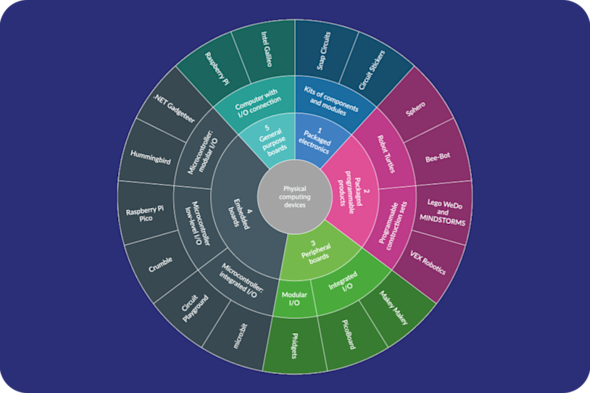
PICRAT framework
Technology integration in the classroom can often feel haphazard or driven by the latest gadgets rather than based on good pedagogy. This Quick Read shows you how to use the PICRAT framework to evaluate your current use of technology and identify specific opportunities to move towards more creative student engagement and transformative teaching practices.
Download PDF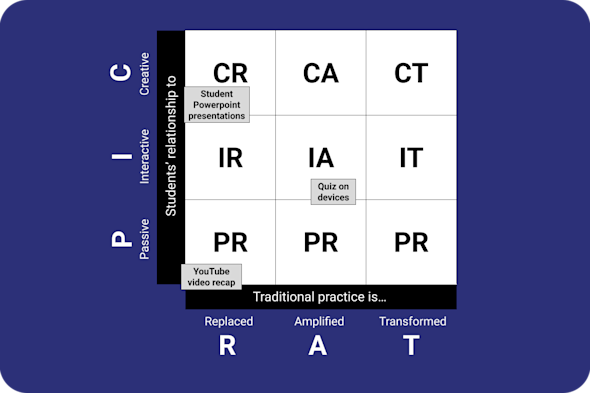
PRIMM
Make sure your programming lessons have a clear pedagogical structure with this Quick Read. Explore how to use the PRIMM framework to move learners through a structured journey from initial prediction to independent creation.
Download PDF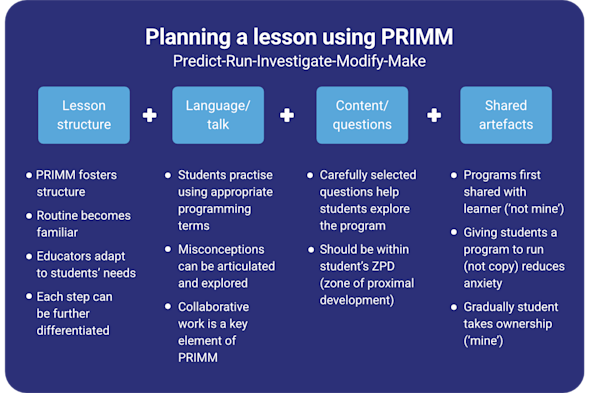
Project-based learning
Project-based learning can help learners stay motivated and focused during long-term, complex computing tasks. This Quick Read explores how to organise learning around the design and evaluation of digital artefacts, making the curriculum feel purposeful, goal-oriented, and relevant to the real world.
Download PDF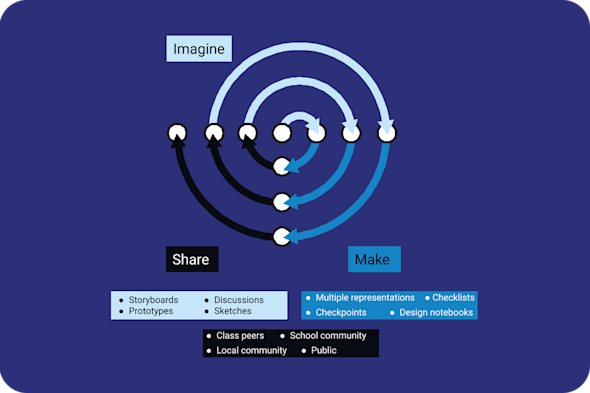
Professional development for computing educators
Sustainable improvements in computing education come from high-quality professional development (PD) for computing educators. Since effective teacher PD is a key driver for better learner outcomes, this Quick Read shares our current perspective on this topic for the benefit of those involved in either delivering or participating in such PD.
Download PDF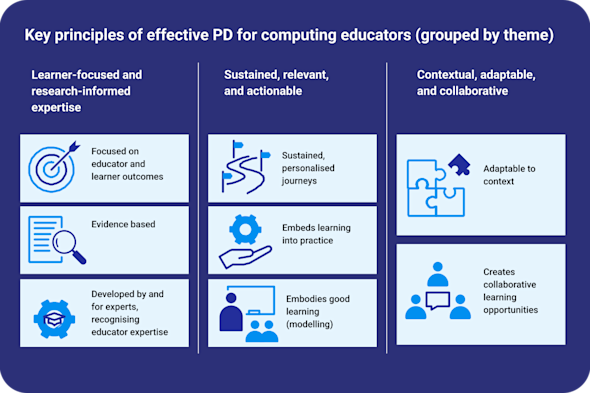
Semantic waves
Using only technical terms to describe concepts can be a barrier to learning. This Quick Read explores how to use semantic waves to guide learners through a structured journey of conceptual understanding, moving between the concrete and the abstract as well as technical and simple, everyday language.
Download PDF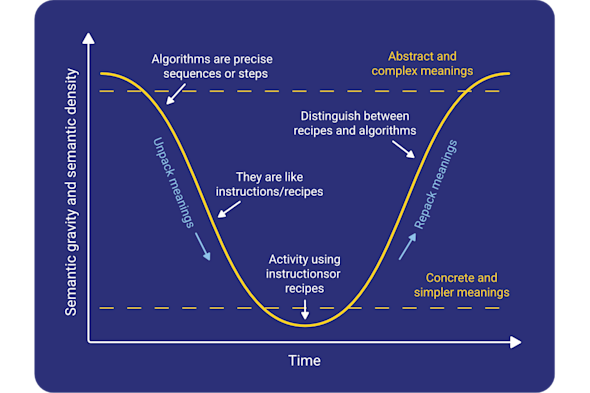
Surveys and interviews
Capturing your learners' genuine thoughts and opinions requires careful planning. Whether you want structured quantitative data or rich qualitative insights, this Quick Read details how to design effective surveys and interviews to gather reliable evidence.
Download PDF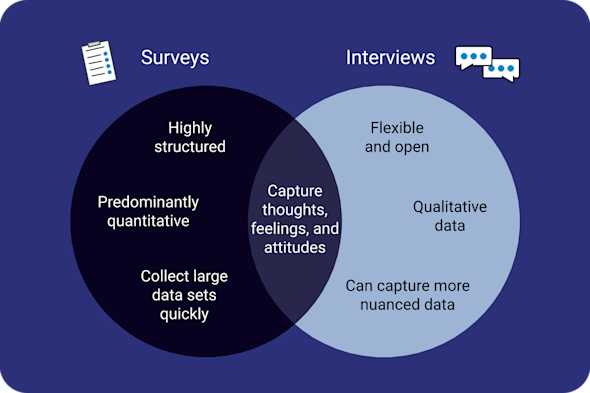
Social learning
Social learning is the process of gaining new knowledge, attitudes, and behaviours by interacting with and observing others. It’s an essential learning method that is practised worldwide, and at every life stage. This Quick Read explores why and how to create social learning opportunities for young people and adults in education or training sessions, online or in person.
Download PDF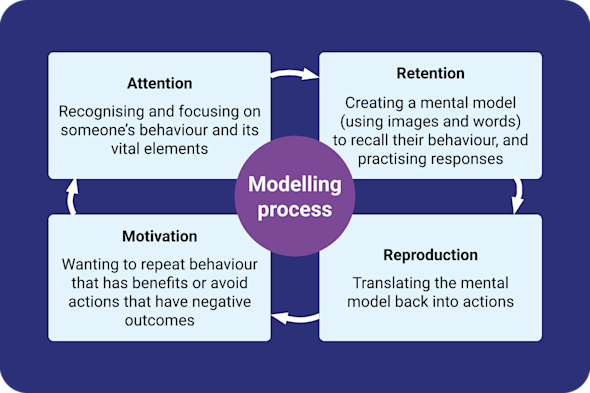
Universal design for learning
Rigid, 'one-size-fits-all' lesson plans often create unintended barriers for learners, especially those with diverse learning needs or disabilities. This Quick Read explores how to use the research-based UDL framework to build flexibility into your instruction, reduce barriers to learning, and significantly increase learner agency for all learners.
Download PDF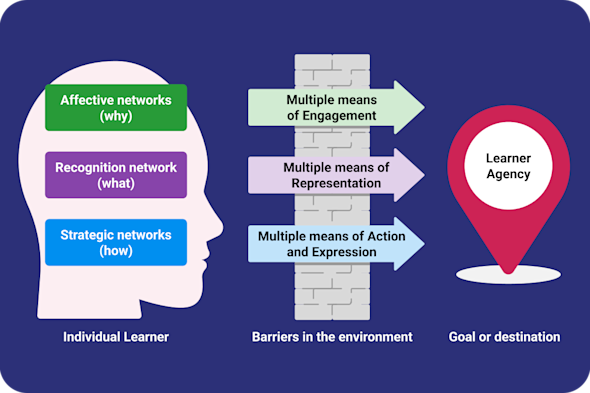
Variety in teaching and assessment
Relying on a single teaching or assessment style can alienate learners who think, learn, and express their knowledge in different ways. This Quick Read explores how to tailor your pedagogical and assessment strategies to suit the unique experiences, needs, and subject matter requirements of your specific learners.
Download PDF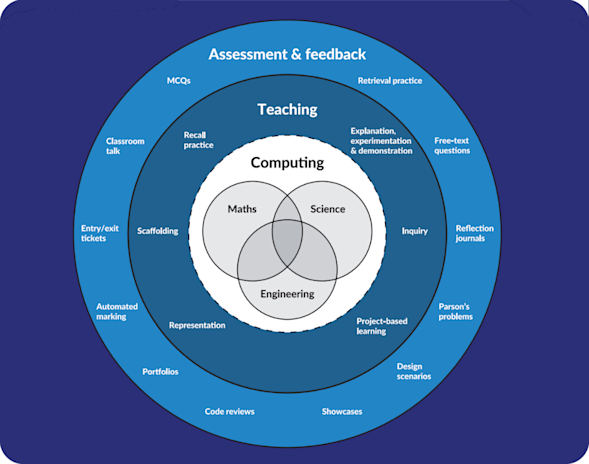
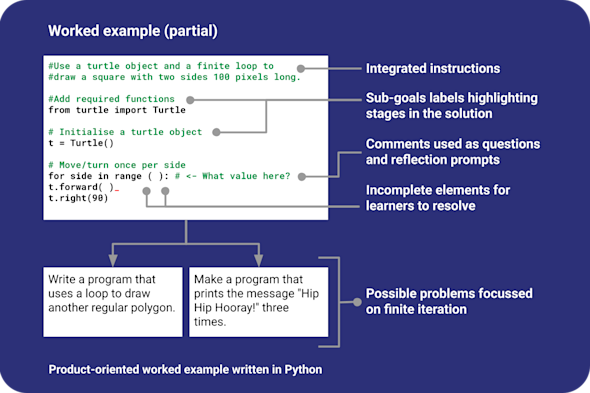
Worked examples
Worked examples can provide a template for learners to follow as they solve new and related problems. This helps reduce cognitive load and increase engagement. This Quick Read explores how to provide worked examples that highlight common structural patterns, giving learners the support they need to build their own solutions successfully.
Download PDF